The Finance tab includes additional fields for tracking Finance related information.
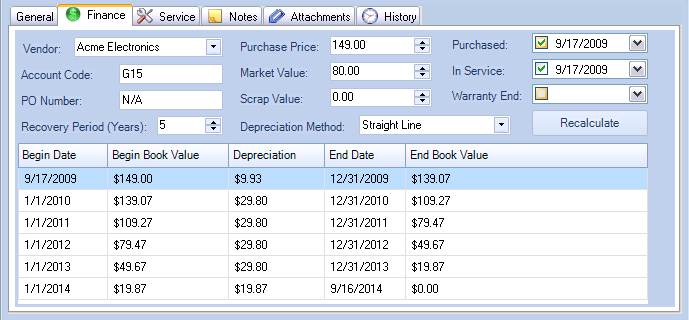
Asset Finance tab
Fields
Field Name |
Description |
Vendor |
A selection field for tracking the Vendor for this asset. Select an existing value, or type in a new value to automatically add a new Vendor to the Vendor list. |
Account Code |
A text field for tracking the account code associated with an asset. You may set the default value for this field by right-clicking on the Asset Type folder and then editing the properties for the asset type. |
PO Number |
A text field for tracking the PO Number associated with the asset. |
Purchase Price |
The price which was paid for the asset. |
Market Value |
The current market value of the asset. |
Scrap Value |
The scrap value of the asset. |
Purchased |
A date field containing the date when the asset was purchased. |
In Service |
A date field containing the date when the asset was placed in service. |
Warranty End |
A date field containing the date when the asset warranty ends. |
Recovery Period |
The expected life of the asset in years. |
Depreciation Method |
The method used to depreciate the asset. |
Depreciation Methods
Straight Line
The Straight Line depreciation method depreciates the asset evenly over time from the beginning book value to the scrap value.
Annual Depreciation Expense = Cost of asset - scrap value / recovery period
For example, an asset purchased for $5500 with a scrap value of $500 and a recovery period of 5 years would depreciate by $1000 per year.
i.e. Annual Depreciation Expense = (5500 - 500)/5 = 1000
The beginning and ending period will be pro-rated according to the number of months the asset was in service for the year.
200% Declining Balance
The Double Declining Balance depreciation method depreciates the asset at twice the Straight Line rate.
Using the example for Straight Line depreciation, the depreciation is $1000 per year, which is 20% (i.e. 1000/5000). The 200% Declining Balance depreciation method depreciates the asset at twice that rate, or 40% (i.e. 2 X 20%). It will be pro-rated according to the number of months the asset was in service for the year.
150% Declining Balance
The 150% Declining Balance depreciation method depreciates the asset at 1.5 times the Straight Line rate.
Using the example for Straight Line depreciation, the depreciation is $1000 per year, which is 20% (i.e. 1000/5000). The 150% Declining Balance depreciation method depreciates the asset at 1.5 times that rate, or 30% (i.e. 1.5 X 20%). It will be pro-rated according to the number of months the asset was in service for the year.
20% Reducing Balance
The 20% Reducing Balance depreciation method depreciates the asset by 20% of the (Book Value - Scrap Value) per year. The depreciation for the last year will be the difference between the Book Value and the Scrap Value so that it will be fully depreciated. Partial periods will be pro-rated according to the percentage of time the asset was in service for the period.
You may add other rates using the menu option Tools --> Manage Selection Fields.
Sum of Years
The Sum of Years depreciation method calculates the depreciation rate on a schedule of fractions based on the sum of the number of years of depreciation.
For example, the sum of years for an asset with a Recovery Period of 5 years is: 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 15. The Sum of Years depreciation method will depreciate the asset over the years as follows: 5/15 for the 1st year, 4/15 for the 2nd year, 3/15 for the 3rd year, 2/15 for the 4th year, and 1/15 for the 5th year. Partial year depreciation will be added in for assets which go in service during the year on a date other than the 1st day of the fiscal year.
See Also